General Opthalmology & Refractive Services
About General Opthalmology & Refractive Services
What is a Refractive error?

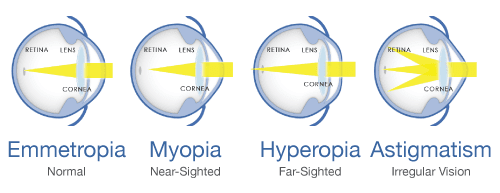
The Various refractive errors are classified as-
- Myopia or near sightedness
- Hyperopia or far sightedness
- Astigmatism
- Presbyopia
What are the symptoms?
- Blurred vision
- Double vision
- Headache
- Eye strain
What are the risk factors?
Genetic
There is evidence to suggest genetic predilection for refractive error. Individuals that have parents with certain refractive errors are more likely to have similar refractive errors.Environmental
Myopia has been observed in individuals with visually intensive occupations.Reading has also been found to be a predictor of myopia in children. It has been reported that children with myopia spent significantly more time reading than non-myopic children who spent more time playing outdoors. Socioeconomic status and higher levels of education have also been reported to be a risk factor for myopia.
The diagnosis of a refractive error is usually confirmed by an eye care professional during an eye examination using a large number of lenses of different optical powers, and often a retinoscope (a procedure entitled retinoscopy) to measure objectively in which the person views a distant spot while the clinician changes the lenses held before the person’s eye and watches the pattern of reflection of a small light shone on the eye. Following that “objective refraction” the clinician typically shows the person lenses of progressively higher or weaker powers in a process known as subjective refraction. Cycloplegic agents are frequently used to more accurately determine the amount of refractive error, particularly in children.
An automated refractor is an instrument that is sometimes used in place of retinoscopy to objectively estimate a person’s refractive error.

What is Myopia?
Myopia or near sightedness is a condition where close objects are clear, and distant objects are blurred. A myopic eye is longer than normal or has a cornea that is too steep, as a result of which the light rays focus in front of the retina.
Myopia is usually inherited and often discovered in childhood. Myopia often progresses throughout the teenage years when the body is growing rapidly.
What is Hyperopia?
Hyperopia or far sightedness is a condition where close objects are more blurred than distant objects. The causes of hyperopia are typically genetic and involve an eye that is too short or a cornea that is too flat, as a result of which images focus at a point behind the retina. Children often have hyperopia, which may lessen in adulthood. In mild hyperopia, distance vision is clear while near vision is blurry. In more advanced hyperopia, vision can be blurred at all distances.What is Astigmatism?
Astigmatism(cylindrical errors) usually occurs when the front surface of the eye, the cornea, has an asymmetric curvature. Normally the cornea is smooth and equally curved in all directions, and light entering the cornea is focused equally on all planes, or in all directions. In astigmatism, the front surface of the cornea is curved more in one direction than in another. This abnormality may result in vision that is much like looking into a distorted, wavy mirror. Usually, astigmatism causes blurred vision at all distances.It can be in combination with myopia or hyperopia.
What is Presbyopia?
After age 40, the lens of the eye becomes more rigid and does not flex as easily. As a result, the eye loses its focusing ability and it becomes more difficult to read at close range. This normal aging process of the lens can also be combined with myopia, hyperopia or astigmatism.What is the treatment of refractive errors?
- Glasses
- Contact lens
- Refractive surgery such as LASIK, ICL
Frequently Asked Questions
When the child holds objects very close to the eye, squeezes to watch TV, or experiences headache while eye strain, the child may be having a refractive error.
The child should be examined once before the age of 3 years to rule out any refractive error.
No.Glass power gets stable once the eyeball stops growing by the age of 18-20 years.